| [1]谢翠柳,刘珂,孟玉坤. 活性氧影响骨重建在骨质疏松发病中的作用[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2013,19(2):178-182.[2]孔祥鹤,牛银波,李宇华,等. OPG/RANK/RANKL系统与骨质疏松研究最新进展[J]. 生命科学研究,2011,15(1):80-85.[3]刘志奎,张柳,穆树林. 血管内皮生长因子在卵巢切除大鼠骨折愈合骨痂中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(41):7605-7608.[4]Tombran-Tink J, Barnstable CJ. Osteoblasts and osteoclasts express PEDF, VEGF-A isoforms, and VEGF receptors: possible mediators of angiogenesis and matrix remodeling in the bone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;316(2):573-579.[5]John S, Brian L, Charles GF. vascular endothelial growth factor regulates osteoblast cell in osteoporotic vertebral fracture. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. 2011;93(SUPP III):246.[6]Street J, Bao M, deGuzman L, et al. scular endothelial growth factor stimulates bone repair by promoting angiogenesis and bone turnover. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(15): 9656-9661.[7]Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9(6):669-676. [8]Keramaris NC, Calori GM, Nikolaou VS, et al. Fracture vascularity and bone healing: a systematic review of the role of VEGF. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 2:S45-57.[9]Ho VC, Duan LJ, Cronin C, et al. Elevated vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2 abundance contributes to increased angiogenesis in vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1-deficient mice. Circulation. 2012;126(6):741-752. [10]Mao-wei Y, Yue Z, Guan-jun T, et al. Effect of fluvastatin on vascular endothelial growth factor in rats with osteoporosis in process of fracture healing. Chin J Traumatol. 2007;10(5): 306-310. [11]Okuno S. Kidney and bone update : the 5-year history and future of CKD-MBD. Bone metabolic marker in hemodialysis patients update. Clin Calcium. 2012;22(7):1009-1017.[12]朱蕾,赵小英,卢兴国. 去卵巢大鼠骨密度变化与骨髓组织血管生成的关系[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2009,9(14):1801-1805.[13]宋亚琪,张柳,骆阳,等. 卵巢切除股骨骨折大鼠骨愈合中降钙素的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(7): 1141-1145.[14]Gerber HP, Vu TH, Ryan AM, et al. VEGF couples hypertrophic cartilage remodeling, ossification and angiogenesis during endochondral bone formation. Nat Med. 1999;5(6):623-628. [15]Carlevaro MF, Cermelli S, Cancedda R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in cartilage neovascularization and chondrocyte differentiation: auto-paracrine role during endochondral bone formation. J Cell Sci. 2000;113 ( Pt 1):59-69. [16]Eriksen EF, Eghbali-Fatourechi GZ, Khosla S. Remodeling and vascular spaces in bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(1): 1-6.[17]Eghbali-Fatourechi GZ, Lamsam J, Fraser D, et al. Circulating osteoblast-lineage cells in humans. N Engl J Med. 2005;352 (19):1959-1966.[18]Zelzer E, McLean W, Ng YS, et al. eletal defects in VEGF(120/120) mice reveal multiple roles for VEGF in skeletogenesis. Development. 2002;129(8): 1893-1904. [19]Keramaris NC, Calori GM, Nikolaou VS, et al. Fracture vascularity and bone healing: a systematic review of the role of VEGF. Injury. 2008;39 Suppl 2:S45-57. PMID:18804573[20]Liu Y, Berendsen AD, Jia S, et al. Intracellular VEGF regulates the balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(9):3101-3113.[21]Pufe T, Scholz-Ahrens KE, Franke AT, et al. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in glucocorticoid-induced bone loss: evaluation in a minipig model. Bone. 2003;33(6): 869-876.[22]Costa N, Paramanathan S, Mac Donald D, et al. Factors regulating circulating vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF): association with bone mineral density (BMD) in post-menopausal osteoporosis. Cytokine. 2009;46(3): 376-381. [23]Chung YS,Hong SH,Min KT,et al. ssociation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene polymorphisms with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures in postmenopausal women. GENES & GENOMICS, 2010; 32(6):499-505[24]Otomo H, Sakai A, Uchida S, et al. Flt-1 tyrosine kinase-deficient homozygous mice result in decreased trabecular bone volume with reduced osteogenic potential. Bone. 2007;40(6):1494-1501. [25]曾敬,徐栋梁,张惠忠,等. 成骨细胞移植促进骨质疏松性骨折愈合过程中相关因子的动态表达[J]. 中国临床康复,2003,7(3): 448-449. [26]刘志奎,张柳,穆树林.血管内皮生长因子在卵巢切除大鼠骨折愈合骨痂中的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011, 14(41): 7605-7608.[27]Martínez P, Esbrit P, Rodrigo A, et al. Age-related changes in parathyroid hormone-related protein and vascular endothelial growth factor in human osteoblastic cells. Osteoporos Int. 2002;13(11):874-881. [28]Ding WG, Wei ZX, Liu JB. Reduced local blood supply to the tibial metaphysis is associated with ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in mice. Connect Tissue Res. 2011;52(1):25-29.[29]初同伟,王正国. 骨折愈合过程中血流量变化与VEGF的相关性研究[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2002,9(6):577-579.[30]杨钦泰,宋琳. 应用VEGF防治肢体严重创伤后骨质疏松的实验研究[J]. 实用骨科杂志,2009,15(3):192-193.[31]Kodama I, Niida S, Sanada M, et al. Estrogen regulates the production of VEGF for osteoclast formation and activity in op/op mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2004;19(2):200-206. [32]Niida S, Kaku M, Amano H,et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor can substitute for macrophage colony-stimulating factor in the support of osteoclastic bone resorption. J Exp Med. 1999;190(2):293-298.[33]Tanaka S, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, et al. Macrophage colony-stimulating factor is indispensable for both proliferation and differentiation of osteoclast progenitors. J Clin Invest. 1993;91(1):257-263.[34]Motokawa M, Tsuka N, Kaku M, et al. Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor-C and -D on osteoclast differentiation and function in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Arch Oral Biol. 2013;58(1):35-41.[35]曹敬,徐栋梁,张惠忠,等. 成骨细胞移植促进骨质疏松性骨折愈合的机制研究[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2003,20(5):439-441.[36]郑青,梁宁. 老年性骨质疏松患者血清细胞因子水平与OPG/RANKL/RANK轴的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2012, 32(17):3651-3653.[37]王强,王坤正,党晓谦,等. 雌激素对去卵巢大鼠骨组织中骨保护素、破骨细胞分化因子和巨噬细胞集落刺激因子mRNA表达的影响[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2006,26(4):532-534.[38]Aldridge SE, Lennard TW, Williams JR, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptors in osteoclast differentiation and function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;335(3):793-798.[39]Nakagawa M, Kaneda T, Arakawa T, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) directly enhances osteoclastic bone resorption and survival of mature osteoclasts. FEBS Lett. 2000;473(2):161-164. [40]Kaku M, Kohno S, Kawata T, et al. Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on osteoclast induction during tooth movement in mice. J Dent Res. 2001;80(10):1880-1883.[41]Wada T,Nakashima T,Hiroshi N,et al.RANKLRANK signaling in osteoclastogenesis and bone disease.Trends in Molecular Medicine,2006,12(1):17-25. |
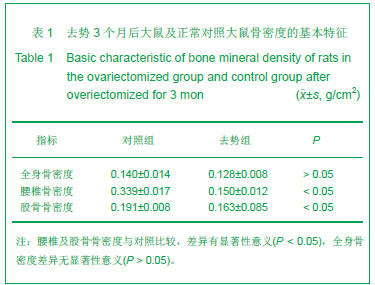

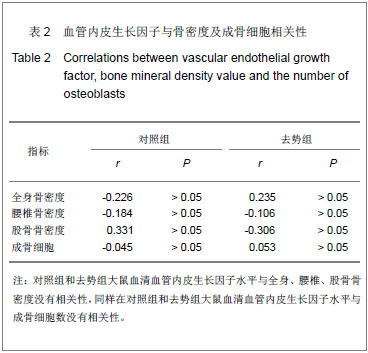
.jpg)